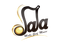Riq Instruments with a Variety of Skins, Cymbals and Gig Bag Cases
The riq (also referred to as the tambourine, daf, or daff, and known as tef in Turkish) is a single-headed frame drum consisting of a skin stretched over a frame with attached jingles (cymbals) inside the frame. The riq serves as a tempo-keeping percussion instrument in Turkish music and has a long and rich history.
Various forms of the tambourine, a type of open drum, have been found among ancient tribes. It spread from the Arabs to Europe through Spain, where it became known as the tambour de basque. Large hoop drums were used in ceremonies in ancient Sumer, while smaller drums were common in Mesopotamia, Egypt, Israel, Greece, and Rome.
Features of Riq
Riq also has several features. A typical riq pulley has a diameter ranging from 20 to 40 centimeters. The width of the pulley can vary between 4 and 6 centimeters. A thin leather cover is stretched to this pulley in one or two places. According to the usage area, purpose, and cultural characteristics of the Riq bells can be attached around it. Riq features are as follows:
- Riq is common in folk music and has been a significant instrument in this genre in Europe for many years.
- Riq is often used to teach music to children and is often used in music created for children's entertainment.
- Riq is traditionally made from a wooden hoop.
- The head of the riq is usually strung on a hoop and then attached to the wooden hoop.
- A traditional tambourine used for an orchestra has 20 pairs of cymbals. This number may be smaller for ensemble tambourines and orchestras.
- Riq usually requires no tuning as the sound of hitting the device is overshadowed by the bells.
- There have been changes to the tambourine since they were first invented, but in most respects, they are still very similar to the original instrument.